Education
Flipped Classroom
The Flipped Classroom is an instructional strategy and a type of blended learning that reverses the traditional learning environment. In this model, instructional content is delivered outside of the classroom, often through online videos or readings, while activities traditionally considered “homework” are moved into the classroom. Key features of the Flipped Classroom include: Students engage […]
Education
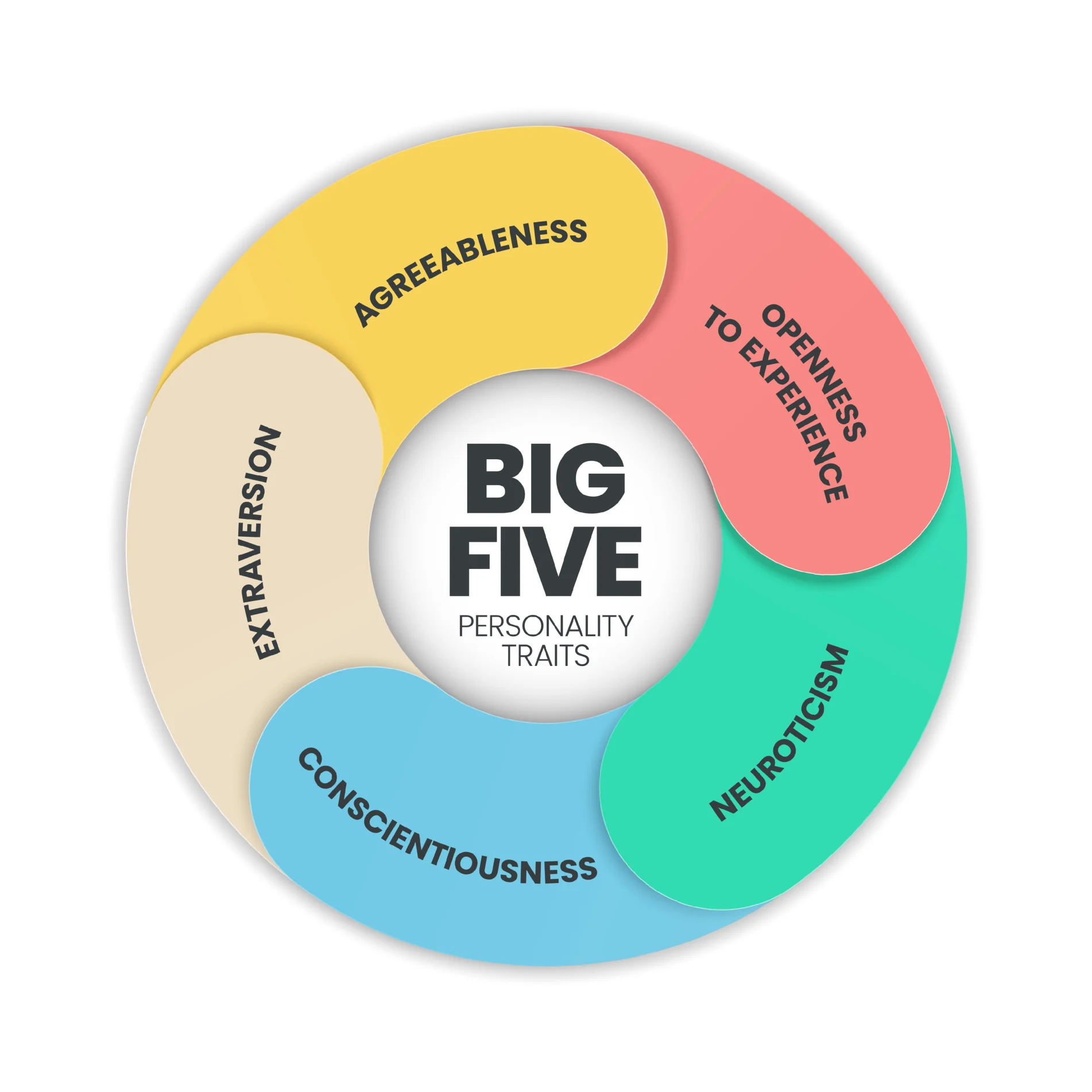
Five-Factor Theory
The Five-Factor Theory, also known as the Big Five personality traits or the OCEAN model, is a widely accepted framework in psychology for understanding human personality. Developed through decades of research, this theory suggests that personality can be described using five broad dimensions: Openness to Experience: This trait reflects curiosity, creativity, and a preference for […]
Education
Expectation Theory
Expectation Theory, also known as Expectancy Theory, is a motivational concept developed by Victor Vroom in 1964. This theory posits that individuals make choices based on their expectations of the outcomes of their actions. It suggests that people are motivated to behave in ways that they believe will lead to desired results. The theory is […]
Education
The Editing Stage
The Editing Stage is a crucial phase in the writing process that follows the drafting and revising stages. During this stage, writers focus on refining the language, style, and technical aspects of their work to prepare it for the final presentation or publication. Key aspects of the Editing Stage include: Grammar and punctuation: Correcting errors […]
Education
The During-Reading Stage
The During-Reading Stage is a critical phase in the reading process where readers actively engage with the text to construct meaning. This stage occurs between the pre-reading and post-reading stages and is crucial for comprehension and analysis. Key strategies for the During-Reading Stage include: Monitoring comprehension: Checking understanding as reading progresses. Visualizing: Creating mental images […]
Education
Dual Code Theory of Memory
The Dual Code Theory of Memory, proposed by Allan Paivio in 1971, suggests that the human mind processes and stores information in two interconnected but distinct systems: verbal and visual. This theory has significant implications for learning and memory. Key aspects of the Dual Code Theory include: Verbal system: Processes and stores linguistic information. Visual […]
Education
Dropout Rate
The Dropout Rate refers to the percentage of students who leave a school or educational institution before completing their program of study. This metric is often used to assess the effectiveness of educational systems and identify areas for improvement. Key aspects of the Dropout Rate include: Calculation methods: Can vary between institutions and countries. Factors […]
Education
The Drafting Stage
The Drafting Stage is a crucial phase in the writing process where the writer creates the initial version of their text. This stage follows the prewriting or planning stage and precedes the revising and editing stages. Key aspects of the Drafting Stage include: Focus on content: Emphasis on getting ideas down rather than perfecting language. […]
Education
Dominant Language
The Dominant Language refers to the primary language used in a multilingual society or by a bilingual individual. It is typically the language that is most widely spoken, has the most social prestige, or is used in official contexts such as government, education, and media. Key aspects of Dominant Language include: Social power: Often associated […]
Education
The Direct Approach
The Direct Approach, also known as the Deductive Approach, is a teaching method where the instructor explicitly presents information, concepts, or rules to students. This approach is often contrasted with inductive or discovery-based learning methods. Key characteristics of the Direct Approach include: Clear learning objectives stated at the beginning of the lesson. Step-by-step instruction and […]