Formulas for Perimeter, Area, and Volume Printable (5th – 8th Grade)
Understanding formulas for perimeter, area, and volume is crucial for students in grades 5-8 as they develop their spatial reasoning and mathematical skills. These concepts form the foundation for more advanced geometry and are applicable in real-world situations.
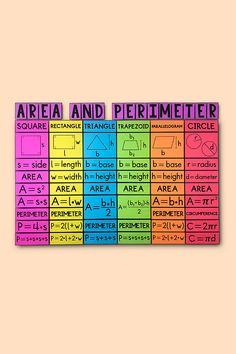
Perimeter Formulas:
- Rectangle: P = 2l + 2w (where l is length and w is width)
- Square: P = 4s (where s is the side length)
- Triangle: P = a + b + c (where a, b, and c are the side lengths)
- Circle: C = 2πr (where r is the radius and π is approximately 3.14)
Area Formulas:
- Rectangle: A = l × w
- Square: A = s²
- Triangle: A = ½bh (where b is base and h is height)
- Circle: A = πr²
- Parallelogram: A = bh (where b is base and h is height)
- Trapezoid: A = ½(b1 + b2)h (where b1 and b2 are parallel sides and h is height)
Volume Formulas:
- Cube: V = s³
- Rectangular Prism: V = l × w × h
- Cylinder: V = πr²h
- Sphere: V = (4/3)πr³
- Cone: V = (1/3)πr²h
- Pyramid: V = (1/3)Bh (where B is the area of the base)
When creating a printable for these formulas, consider including visual representations alongside each formula. For example, show a labeled diagram of a rectangle next to its perimeter and area formulas. This helps visual learners connect the abstract formula with the concrete shape.
Organize the formulas by category (perimeter, area, volume) and complexity. Start with simpler shapes like squares and rectangles before moving on to more complex shapes like trapezoids or spheres. This progression allows students to build on their understanding gradually.
Include a brief explanation or real-world application for each formula to help students understand its relevance. For instance, mention how the area formula for a rectangle could be used to calculate how much carpet is needed for a room.
Consider adding practice problems or blank spaces where students can write their own examples. This interactive element encourages active engagement with the material.
Remember to include a reminder about units of measurement. Perimeter is measured in linear units (e.g., cm, m), area in square units (e.g., cm², m²), and volume in cubic units (e.g., cm³, m³).
Lastly, include a section on common conversions between units, such as converting between cm² and m², as this is often a stumbling block for students in this age group.
By providing a clear, visually appealing, and comprehensive printable of these formulas, you’ll be giving students a valuable reference tool for their mathematical journey through middle school and beyond.




