Education
Systematic Transcription
Systematic transcription is a methodical approach to converting spoken language or audio recordings into written text. This process is crucial in various fields, including linguistics, qualitative research, and speech therapy. It involves not only capturing the words spoken but also noting relevant non-verbal cues, pauses, and other contextual information. Key elements of systematic transcription: Verbatim […]
Education
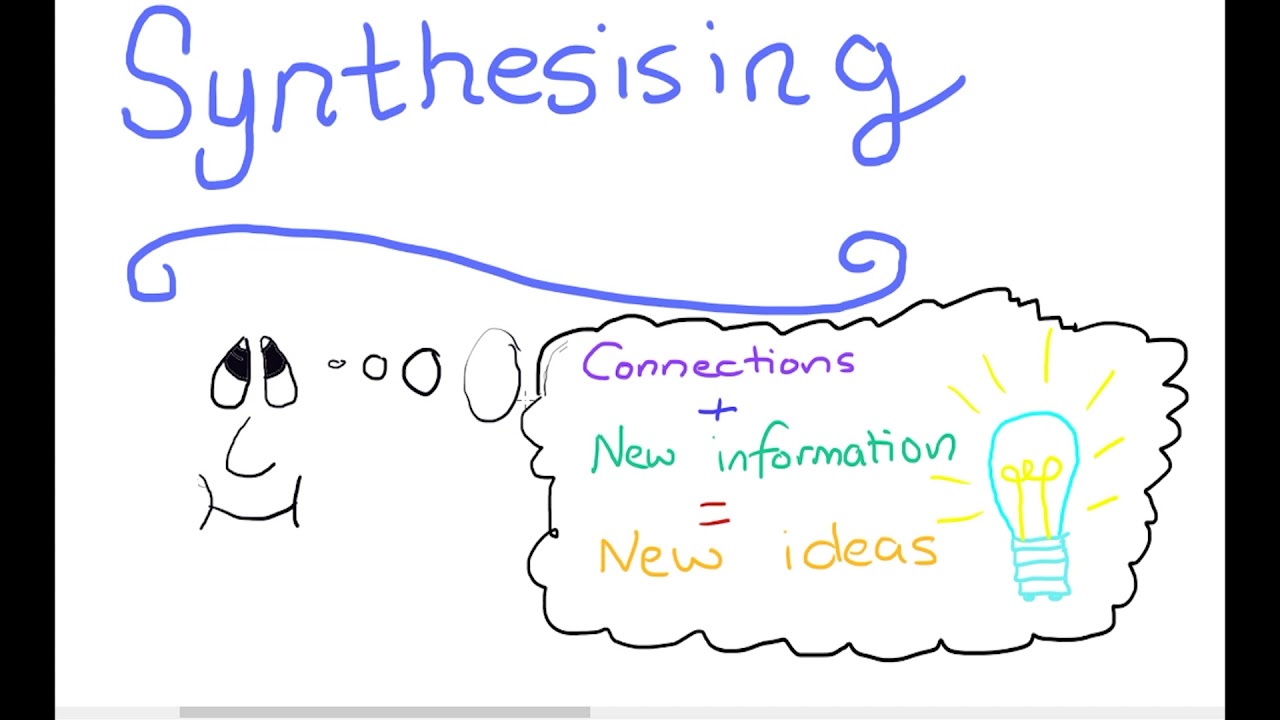
Synthesizing
Synthesizing is a higher-order cognitive skill that involves combining various pieces of information, ideas, or concepts to create a new, cohesive whole. This process goes beyond mere summarizing or comparing; it requires the ability to integrate diverse elements and generate original insights or solutions. Key aspects of synthesizing: Identifying connections between different ideas or sources […]
Education
Syntax
In linguistics and language education, syntax refers to the set of rules governing the structure of sentences in a language. It deals with how words and phrases are arranged to create meaningful expressions and convey complex ideas. Key elements of syntax include: Word order (e.g., subject-verb-object in English) Phrase and clause structure Agreement between sentence […]
Education
Synchronous E-Learning
Synchronous e-learning refers to a form of online education where learners and instructors interact in real-time, despite being physically separated. This approach leverages technology to create a virtual classroom environment, allowing for immediate feedback, discussion, and collaboration. Key features of synchronous e-learning: Real-time interaction between participants Live video or audio conferencing Instant messaging and chat […]
Education
Symbolic Analogy
Symbolic analogy is a cognitive process and problem-solving technique that involves drawing parallels between seemingly unrelated concepts or situations. This approach uses symbols or abstract representations to highlight similarities in structure or function between different domains. Key aspects of symbolic analogy: Identification of shared attributes or relationships Transfer of knowledge from a familiar domain to […]
Education
Summarizing
Summarizing is a crucial cognitive skill that involves distilling the main ideas and key points from a larger body of information. This process requires the ability to identify essential concepts, discard less relevant details, and concisely express the core message. Benefits of summarizing include: Improved comprehension and retention of information Development of critical thinking and […]
Education
Successive Relearning
Successive relearning is an evidence-based learning strategy that combines two powerful techniques: retrieval practice and spaced repetition. This method involves repeatedly studying and testing oneself on the same material over increasing time intervals, enhancing long-term retention and recall. Key principles of successive relearning: Initial learning through study and self-testing Repeated retrieval attempts at gradually increasing […]
Education
Successful Intelligence
Successful intelligence, a concept developed by psychologist Robert Sternberg, proposes that success in life is achieved through a balanced combination of analytical, creative, and practical abilities. This theory challenges traditional notions of intelligence that focus primarily on academic skills measured by IQ tests. The three components of successful intelligence are: Analytical intelligence: Problem-solving and critical […]
Education
Subject-Centered Curriculum
A subject-centered curriculum is an educational approach that organizes learning around specific academic disciplines or subjects. This traditional model of curriculum design focuses on imparting knowledge and skills within well-defined subject areas, such as mathematics, science, literature, and history. Characteristics of a subject-centered curriculum include: Clear division of knowledge into distinct subjects Emphasis on mastery […]
Education
Subconscious Underachieving
Subconscious underachieving is a psychological phenomenon where individuals unconsciously perform below their true potential. This behavior often stems from deep-seated fears, self-doubt, or negative beliefs about one’s abilities. Unlike conscious underachievement, where a person deliberately chooses not to excel, subconscious underachievers are often unaware of the internal barriers holding them back. Key aspects of subconscious […]